This work by New American History is licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) International License. Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at newamericanhistory.org.
Is the Rule of Law Essential to “The Perpetuation of Our Political Institutions”?
Read for Understanding
The Jacksonian era, 1820-1845, was a time of rapid change in the United States. Westward expansion by white settlers, the dispossession of Indigenous peoples, and expanding slavery coincided with establishing the Rule of Law in these formerly tribal-held lands and challenged the ideas on which the United States was founded. Abraham Lincoln was a young man during this time, and he was living in Illinois, which was then considered the western frontier. Investigating Lincoln’s first public speech in 1838, which we call his Lyceum Address, can help us understand this period of transition in U.S. history and make connections to questions we are still asking in the 21st century.
Key Vocabulary
Chattel slavery - the enslaving and owning of human beings and their offspring as property, able to be bought, sold, and forced to work without wages
Due Process of Law - fair treatment through the regular judicial system, especially as a citizen's entitlement.
Extra-Judicial Violence - using force or harm outside of the legal system, like when someone takes the law into their own hands instead of relying on the courts or police; sometimes described as vigilantism or vigilante violence
Forum - a place, meeting, or medium where ideas and views on a particular issue can be exchanged.
Lyceum - an institution for popular education providing discussions, lectures, concerts, etc.
Mob Law - The rule of the mob or the disorderly classes; violent usurpation of authority by the rabble; sometimes called “lynch law”
Mob Violence – when a large group of people acts aggressively or violently together, often causing harm, damaging property, or engaging in destructive behavior due to strong emotions like anger or frustration
Perpetuation – the continued existence or maintenance of something over time
Political Institutions – the organized structures and systems that help make and enforce rules and decisions in a community or country, like governments, courts, and elected offices
Rule of Law - the principle that everyone, including leaders and citizens, must follow the same set of fair and consistent rules to ensure justice and order in a society
Engage:
How might we use current technologies to help us understand the past without losing the author's voice in our primary source documents?
Have you ever thought about why and how we live by a set of rules or laws that we agree upon? This learning resource digs deep into the very first speech Abraham Lincoln delivered and asks big questions about how we govern ourselves and how we do or don’t recommit to the ideals of the Revolution and the early Republic. Because Lincoln’s speech was delivered in 1838 - almost 200 years ago - and because he was addressing big ideas, reading and understanding the speech is HARD WORK for our 21st-century brains. It’s worthwhile to spend time with it, though, because the ideas continue to resonate even today. To make the speech more accessible, we have used AI to rewrite the speech for a present-day reader.
Start by reading the first few paragraphs of the Lyceum speech. Remember that there are two versions of the speech in the document: one in Lincoln’s words and one rewritten for a contemporary audience. (You can read the full speech rewritten for today here and read the original words here.) Turn and talk to an elbow partner, or if working remotely, your teacher may provide access via video conferencing in a breakout room or a collaborative tool such as Google Docs or Google Slides.
- How does reading the speech in 21st-century English change your understanding of the original paragraphs?
- What understanding and meaning might be lost if you only read the paragraphs in their 21st-century rewriting?
- What might you lose or gain by reading an old speech by a famous leader using ChatGPT?
Learn more about the context of Lincoln’s Lyceum Address by watching the video Fortifying Democracy, Part 1. The scholars in the video represent historians, political scientists, and scholars of rhetoric.
In the video, Dr. Saladin Ambar describes Lincoln’s speech as “profoundly prophetic,” meaning that it predicted what would happen in the future.
Turn and talk to a partner, or if working in a remote learning environment, your teacher may allow you to use videoconferencing or a collaborative document such as Google Docs to collaborate.
How might the words we read today resonate with the political situation in our own time?
Your teacher may ask you to record your answers on an exit ticket.
Explore:
How might we better understand what motivates acts of mob violence, and how might that inform how we prevent it?
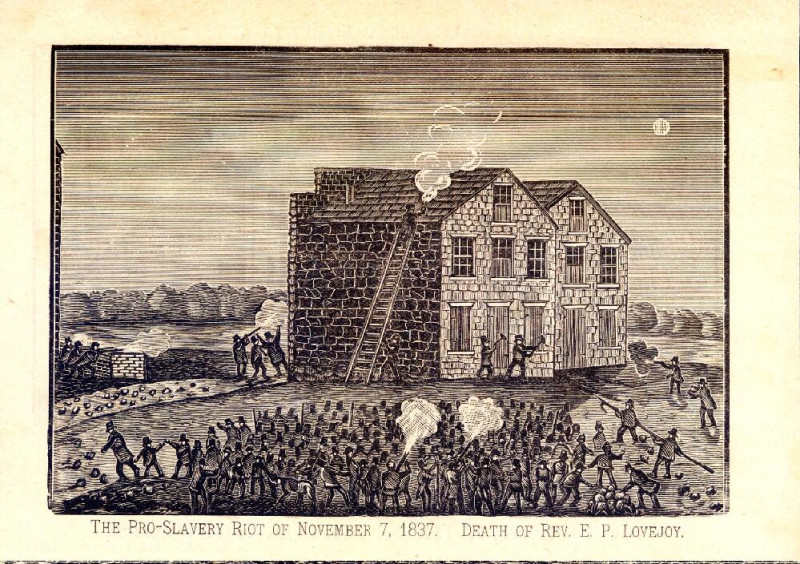
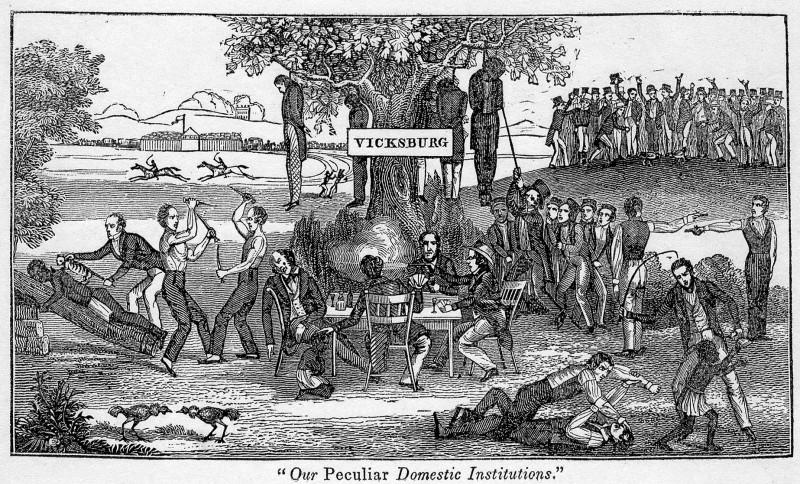
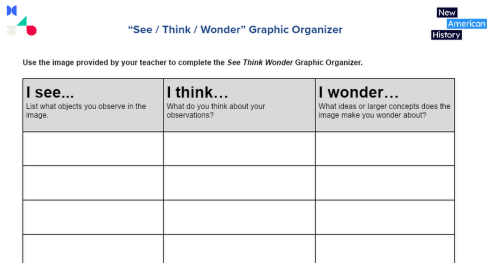
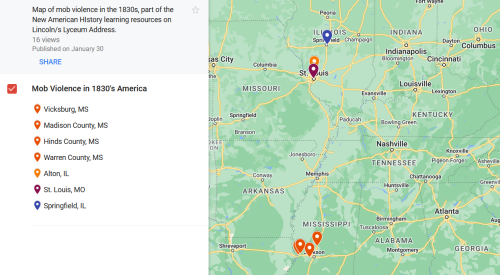
In Lincoln’s speech, he refers to three instances of mob violence that had taken place in recent years in what were then the western states of Illinois, Missouri, and Mississippi. (Can you imagine a time when the mid-west and mid-south were considered the western frontier?) Use the See Think Wonder graphic organizer to explore this map and the following images.
(WARNING: MAP AND IMAGES MAY CONTAIN GRAPHIC IMAGES OF RACIAL VIOLENCE - PLEASE USE CAUTION.)
Share your See, Think, Wonder observations with the rest of the class, or turn and talk with a classmate. If you are learning remotely, your teacher may allow you to use this Google Slides template as a collaboration tool (make a copy of the template for yourself).
Your teacher may ask you to record your answers on an exit ticket.
Explain:
What might cause people to opt for mob rule over the rule of law? How does Lincoln suggest Americans respond?
As European settlers moved west into what is now the mid-west and mid-south, they were building new communities made up of people who had a range of ideas about the value of the Rule of Law. Disagreements about the expansion of chattel slavery into the western settlements and the displacement of indigenous nations created a lot of disagreement and tension for the settlers, in addition to trying to transplant the ideas of the Revolution and the Constitution into new lands.
To learn more about some examples of Mob Rule, where people threw off the yoke of the Rule of Law and decided to take it into their own hands, watch Fortifying Our Democracy, Part 2. You’ll also learn what Abraham Lincoln thought about Mob Rule.
Then read this excerpt from Lincoln’s speech and use the First, Then, Finally graphic organizer to make sense of the passage. Follow the Reflect and Discuss prompts (both in the First, Then, Finally slides and also below) to make meaning of his words.
Reflect and Discuss
- What is Lincoln suggesting in the last sentence of the paragraph? What risk worries him if mobs and their passions rule? What does he mean by “walls”?
- What Lincoln is describing is the opposite of the Rule of Law. What do we mean by the Rule of Law v. the Rule of Mob? What might cause people to opt for mob rule?
Next, as you look at the sources below, make sure to take into consideration the points of view that the source represents. Why might different groups of people have differing perspectives on these events that seem so clearly wrong to us today? Consider geography and date of publication, among other factors, as you examine each source. Also, consider if it is a primary or secondary source. How do you decide?
These sources describe in words and images terrible things that people did to other humans in the 1830s. Do we still encounter things like this today?
After completing the graphic organizer, decide on a primary or secondary source to share with the rest of the class to explain what happened.
Primary and Secondary Sources
Elijah Lovejoy Murder, Alton, IL
- 1948 St. Louis Star & Times Essay: Lovejoy, Who Died at Alton, Martyr for Press Freedom (Transcription here)
Francis McIntosh Lynching, St. Louis, MO
Vicksburg, MS, Lynchings
- Vicksburg Letter in Defense of Citizen Actions, August 1, 1835 [reprinted in the United States Gazette, Philadelphia] (Transcript Here)
- Commentary on Vicksburg from The Liberator, Boston, August 8, 1835 (Transcript Here)
Use this choice board to determine which kind of presentation you want to create. Each presentation will focus on three themes:
- Describe what happened, from the perspective of the person or people who were attacked, and from the perspective of the people who were attacking others.
- Emphasize: Why did the mob think it needed to act beyond the rule of law?
- Explain: The different points of view expressed by the people who created the source and why they might have taken that perspective on the event
Your teacher may ask you to record your answers on an exit ticket.
Elaborate:
How might we evoke the commitment of the Founding Era in people today?
Benjamin Franklin described the U.S. government as, “a republic, if we can keep it.” Can people far removed from an event like the American Revolution fully appreciate what it takes to “keep” a republic?
In this section, you’ll learn more about the Lyceum address with the third Fortifying our Democracy video, focusing on Lincoln’s advocacy for the Rule of Law and his warning about the possibility of a tyrant coming to power if the Rule of Law is not followed.
As you watch Fortifying Democracy, Part 3, consider these questions:
- What does Lincoln suggest about the risk and hope of democracy, the farther we get from the country’s founding?
- As the United States approaches the 250th anniversary of its founding in 2026, what risks are we facing, and how might these be connected to Lincoln’s predictions and his recommendations?”
- “How might we evoke the commitment of the Founding Era in people today?”
Dig into Lincoln’s own words (and/or a version of the speech adapted for middle school readers), using the following questions to guide your discussion as you read along.
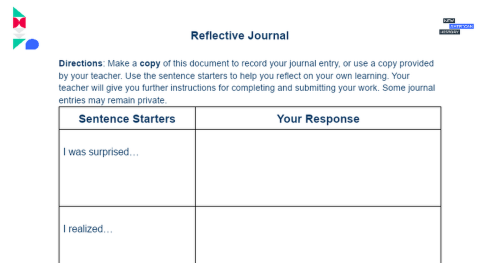
Use your responses to elaborate using a reflective journal entry.
- How, if at all, are Lincoln’s words still relevant today? How does the tension between passion and reason still play out in our political institutions? Give at least one concrete example.
Your teacher may ask you to record your answers on an exit ticket.
Extend:
Have there been moments of change or re-imagination so profound that they count as “re-founding” in U.S. history?
In his biography of Martin Luther King, Jr., Jonathan Eig wrote, “On December 5, 1955, a young Black man became one of America’s founding fathers. He was twenty-six years old and knew the role he was taking carried a potential death penalty.”
In his biography of Martin Luther King, Jr., Jonathan Eig wrote, “On December 5, 1955, a young Black man became one of America’s founding fathers. He was twenty-six years old and knew the role he was taking carried a potential death penalty.”
Think about what you know of the history of the United States. Identify an example of when the country has needed to recommit to its original principles – perhaps we can describe this as a “re-founding.” Some of these might be instances of Constitutional amendments, but others might be times or events when big changes happened - perhaps through Supreme Court decisions.
Create a tabletop exhibition, using at least three primary source images, documents, or recordings, that argue that an event or moment in U.S. history constitutes a “re-founding” and recommitment at a particular moment in U.S. history or by a particular figure in U.S. History. You can find more information about creating an exhibition here, in a toolkit from PBLWorks.
We would love to see images of your exhibits! Feel free to share them with us either through your school's social media account (if your school permits) or via email: editor@newamericanhistory.org
Your teacher may ask you to record your answers on an exit ticket.
Citations:
American Anti-Slavery Almanac. “Illustrations of the American anti-slavery almanac for 1840.” New York, New York. United States New York, 1840. New York. Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007680126/.
American Anti-Slavery Society. “Particulars of the massacre,” Emancipator Extra. December 1, 1837. https://newseumed.org/tools/artifact/emancipator-details-fatal-shooting-elijah-lovejoy.
Basler, Roy, ed. “Lyceum Address,” The Collected Works of Abraham Lincoln, Vol. 1. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1953. https://quod.lib.umich.edu/l/lincoln/lincoln1. Accessed February 7, 2024.
Bouie, Jamelle. “If Destruction Be Our Lot, We Muse Ourselves Be Its Author and Finisher,” New York Times. February 3, 2024. https://www.nytimes.com/2024/02/03/opinion/abraham-lincoln-ambition-speech.html?unlocked_article_code=1.Tk0.Xlze.dfKFWrkMstIA&bgrp=g&smid=url-share. Accessed February 5, 2024.
Charleston Daily Courier, The. “From the Vicksburg Register,” The Charleston Daily Courier. Charleston, SC. July 28, 1835. https://www.newspapers.com/image/604393030. (Subscription required.)
Eaton, Foster. “Lovejoy, who died at Alton, a martyr for press freedom,” St. Louis Star & Times. St. Louis, MO. June 11, 1948. https://www.newspapers.com/image/205513811. (Subscription required.)
Eig, Jonathan. King: A Life. New York, NY: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 2023.
Liberator, The. “Postscript from the Natchez Courier, July 10,” The Liberator, Boston. Boston, MA. August 8, 1835. https://www.newspapers.com/image/34584443. (Subscription required.)
Lincoln Presidential Foundation. 2023. "Fortifying our democracy: Lincoln’s Lyceum Address." Video Series. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLR5Dwi_NdBZGhM7l1EAsoMOZk-xmLTbWK.
McNamara, Robert. "American Lyceum Movement." ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/american-lyceum-movement-1773297 (accessed January 23, 2024).
National Banner and Nashville Whig. “Horrible tragedy,” National Banner and Nashville Whig, Nashville, TN. May 11, 1836. https://www.newspapers.com/image/603851488. (Subscription required.)
National Constitution Center. 2018. “Doris Kearns Goodwin explains Lincoln’s Lyceum Address.” Video Interview. YouTube. https://youtu.be/M1LWKm_z_go?si=1y5kGc2KO9msi5Tt.
Norton, W.T., publisher. “The pro-slavery riot of November 7, 1837, Alton, Ill. Death of Rev. E.P. Lovejoy,” 1909 postcard from a woodcut made in 1838. Robert Langmuir African-American Photograph Collection, Stuart A. Rose Manuscript Archives and Rare Book Library, Emory University Libraries. https://digital.library.emory.edu/catalog/535t76hdtx-cor.
Reparative Justice Coalition of St. Louis. “The lynching of Francis McIntosh,” Reparative Justice Coalition of St. Louis, 2022. https://www.rjcstl.org/francis-mcintosh-remembrance.
Reparative Justice Coalition of St. Louis. "Mob violence and racial terror: the lynching of Francis McIntosh." University of Missouri - St. Louis Digital Humanities Lab, 2020-2022. https://www.umsldigitalhumanities.org/francismcintosh/s/francismcintosh/page/introduction.
Richardson, Heather Cox. “Letters from an American,” January 27, 2024. https://heathercoxrichardson.substack.com/p/january-27-2024 (Accessed January 28, 2024.)
Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture, Manuscripts, Archives and Rare Books Division, The New York Public Library. "Our peculiar domestic institutions." New York Public Library Digital Collections. Accessed February 18, 2024. https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/510d47da-7537-a3d9-e040-e00a18064a99
"The Pro-Slavery Riot on November 7, 1837. Death of Rev. E. P. Lovejoy." Wood engraving by unknown, ca. 1838. Missouri History Museum Photograph and Prints collections. Illinois. N29376. Accessed February 4, 2024. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:%22The_Pro-Slavery_Riot_on_November_7,_1837._Death_of_Rev._E._P._Lovejoy.%22.jpg
United States Gazette, The. “The Vicksburg tragedy,” The United States Gazette, Philadelphia. August 1, 1835. https://www.newspapers.com/image/605024090. (Subscription required.)